Have you ever wondered what Malware is, what types exist, the dire consequences it can unleash, and of course, how you can defend yourself against these virtual threats? No? Well, let’s talk about Malware then!
What is Malware?
The term “malware” comes from the combination of the words “malicious” and “software,” and refers to any type of software designed to harm, infect, or infiltrate computer systems without the user’s consent. Cybercriminals use malware for a wide range of nefarious purposes, from stealing valuable information to disrupting online services and extorting victims.
The term “Malware” encompasses various types of malicious software such as Viruses, Trojans, Worms, Ransomware, Spyware, and Adware.
Types of Malware and Their Characteristics
Virus
Viruses are one of the oldest and most recognizable forms of malware. They attach to executable files and spread when users run these files. Once inside the system, a virus can replicate and spread to other files and programs. Viruses can damage or corrupt files, slow down system performance, and in some cases, render it unusable. A historical example is the “Brain” virus, identified in 1986, which spread through floppy disks.
Trojans
Trojans appear as legitimate or harmless software but hide a malicious purpose. Once users download and install these programs, Trojans can provide attackers with remote access to the compromised system. This allows cybercriminals to steal confidential information, install other malware, or even control the computer remotely. The “Zeus” Trojan, used for stealing banking information, is a notable example in this category.
Worms
Worms are self-replicating and do not need executable files to spread. They exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks to spread rapidly. Worms can overload networks and slow down system performance. A historical example is the “Conficker” worm, which infected millions of computers in 2008 by exploiting a vulnerability in Windows systems.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts the user’s files and demands a ransom, usually in cryptocurrencies, to unlock them. Ransomware attacks can cripple businesses and individual users, as essential files become inaccessible. One of the most impactful examples is the “WannaCry” attack in 2017, which affected healthcare systems, businesses, and public services worldwide.
Spyware
Spyware hides in systems and monitors user activities without their knowledge. It can collect personal information, browsing logs, and passwords, and then transmit them to attackers. Cybercriminals can use this information for identity theft, financial fraud, and other cybercrimes. A common example of spyware is the “Keylogger,” which records keystrokes to capture passwords and sensitive data.
Adware
Adware, though less harmful than other types of malware, can be extremely annoying. Its aim is to display unwanted ads to users, often redirecting them to malicious websites or collecting information about their browsing habits to target advertising. Some adware can also slow down system performance. An example is the “Superfish” adware that came pre-installed on Lenovo laptops and displayed ads to users.
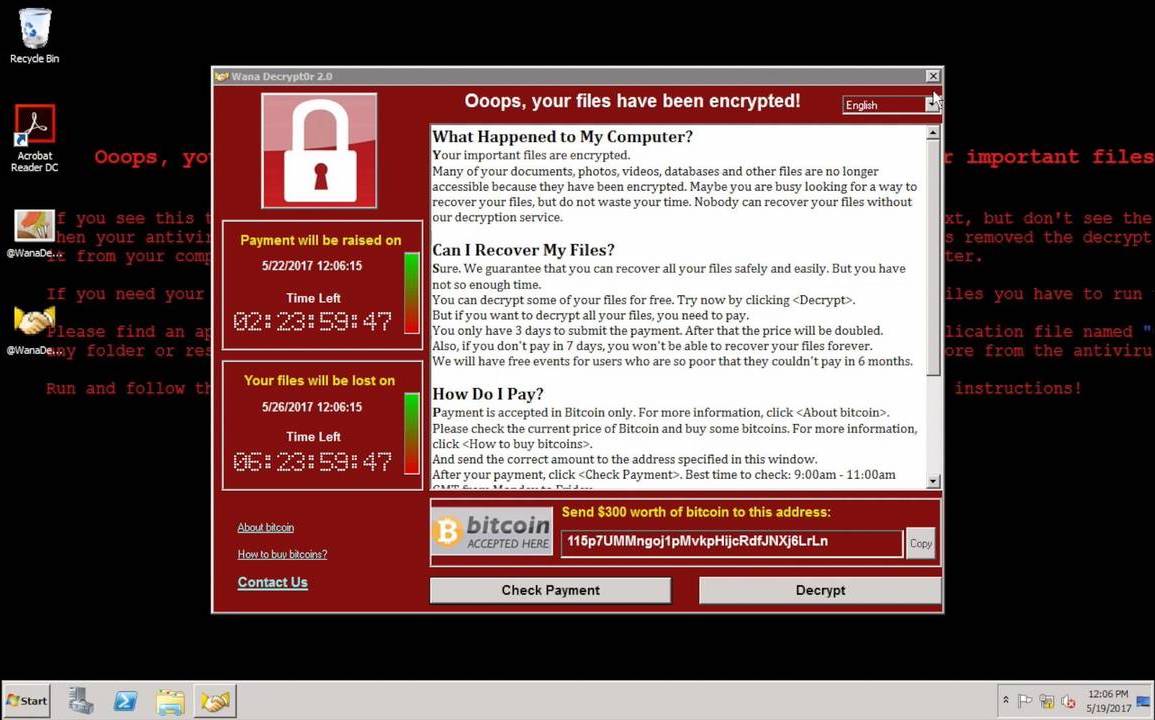 Screenshots of the WannaCry ransomware in action. Source: Google
Screenshots of the WannaCry ransomware in action. Source: Google
Damaging Consequences of Malware
Malware can have significant repercussions for individuals, businesses, and society at large. Some negative consequences that may arise as a result of malware infection include:
Loss of Sensitive Data
One of the most dreaded impacts of malware is the loss of critical data. The most destructive types of malware, such as ransomware, can encrypt important files and demand a ransom for their release. If victims cannot pay or do not obtain a valid decryption key, they may irreparably lose their data, including personal documents, photos, and work files.
Identity Theft and Financial Fraud
Spyware and other types of malware can gather personal information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, and banking details. Attackers can use this information to commit identity theft, make fraudulent purchases, and access financial accounts. Victims may face long-term financial problems and a difficult process to recover their identity.
Disruption of Business Operations
Businesses can face critical shutdowns due to malware attacks. A successful ransomware attack can immobilize essential systems, halt production, and cause substantial financial losses. Prolonged disruptions can also damage a company’s reputation and customer trust.
Privacy Breach
Spyware and other types of malware can seriously compromise users’ privacy. By monitoring online activities and collecting personal data, attackers can gain intimate details about a person’s life. This can lead to embarrassing situations or even extortion if attackers threaten to reveal compromising information.
System Performance Degradation
Some types of malware, like adware, can significantly slow down the performance of computers and devices. Unwanted ads and redirects to malicious websites can make browsing frustrating and less efficient. This can affect productivity and the user experience.
Social and Economic Effects
Large-scale malware attacks can have social and economic impacts. For example, a ransomware attack affecting a hospital could jeopardize patients’ lives and cause chaos in the healthcare system. Additionally, attacks disrupting online services can affect public trust in digital security and the economy as a whole.
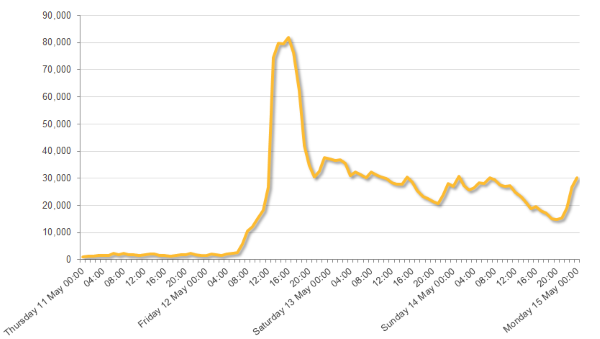 Number of machines affected by the WannaCry ransomware. Source: Symantec
Number of machines affected by the WannaCry ransomware. Source: Symantec
Protection and Prevention Measures
Antivirus and Antimalware Software
Use an updated and reliable antivirus and antimalware solution. These programs scan and detect threats in real-time, helping you avoid malware infections. Keep these programs updated to address new threats.
Regular Software Updates
Keep your operating systems, programs, and applications up to date. Patches and updates often include security fixes that address known vulnerabilities attackers could exploit.
Downloads from Trusted Sources
Only download software and applications from official and trusted sources. Avoid third-party websites and downloads of questionable origin, as they may hide malware in legitimate appearances.
Exercise Caution with Email
Do not open attachments or click on links in suspicious emails or from unknown senders. Attackers often use phishing tactics to distribute malware through deceptive messages.
Regular Backup
Perform periodic backups of your important files to external devices or the cloud. In the event of a malware infection, having up-to-date backups will allow you to restore your data without paying ransoms.
Cybersecurity Education
Stay informed about the latest threats and attack tactics. Cybersecurity education will help you recognize potential risks and make informed decisions to protect yourself.
In summary, malware is one of the primary threats in the digital world. Its constant evolution demands that users remain vigilant and take preventive measures to safeguard themselves. With knowledge and caution, you can effectively defend against malware and enjoy a safer online environment. Remember, security starts with each one of us!
